Introduction:
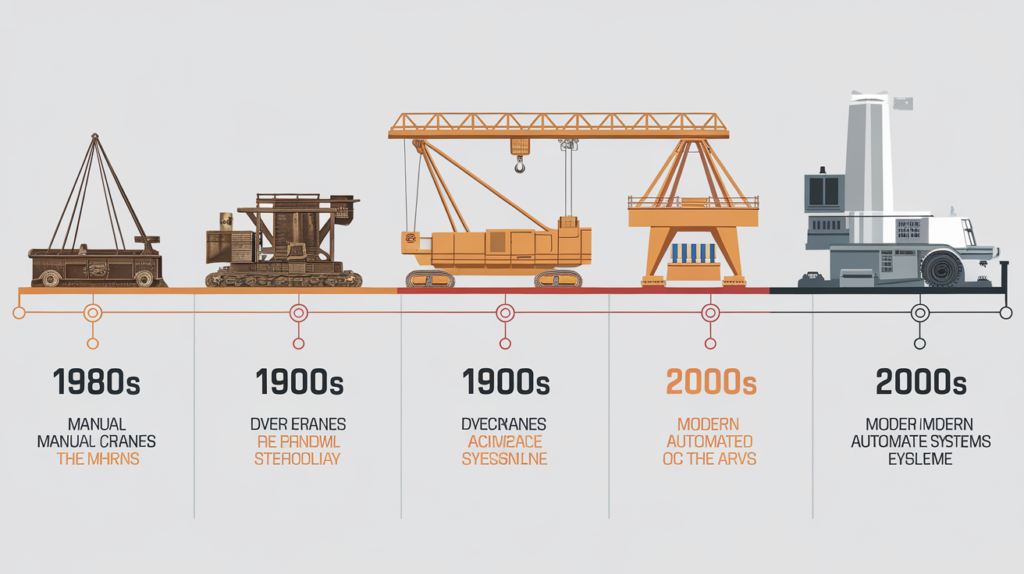
Crane technology has undergone a remarkable transformation over the centuries, evolving from simple manual operations to highly automated and intelligent systems. From building ancient wonders to facilitating modern-day industrial projects, cranes have played a crucial role in heavy lifting and construction. This blog takes a deep dive into the journey of crane technology and explores how advancements in automation and engineering are revolutionizing industries worldwide. Whether you’re in construction, manufacturing, or logistics, understanding crane technology’s progression can help businesses make better, more efficient choices in lifting solutions.
The Early Days of Crane Technology
Crane technology dates back to ancient civilizations. Early cranes were powered by human and animal labor, using pulleys and levers to lift heavy objects. These manual cranes were primarily used to construct monumental structures such as the pyramids of Egypt and the Parthenon in Greece. While effective for their time, manual cranes were limited in capacity and required large teams of laborers to operate.
With the advent of the Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries, steam-powered cranes debuted. This marked a significant turning point in crane technology, allowing for heavier loads to be lifted with less human effort. These steam-powered cranes were commonly used in shipbuilding and large-scale construction projects.
The Introduction of Electrification and Mechanization
The 20th century saw the introduction of electric motors in cranes, which brought about a new era of efficiency and safety. Electric-powered cranes could handle heavier loads more precisely and with greater ease, reducing the risk of human error and injury. By the mid-20th century, hydraulic systems were incorporated into cranes, further enhancing their lifting capacity and operational smoothness.
At this point, cranes were becoming more versatile, with specific designs emerging for different industries. Overhead cranes, gantry cranes, and tower cranes became popular in factories, ports, and construction sites, respectively. The mechanization of cranes drastically reduced manual labor and increased productivity, setting the stage for future innovations in automation.
The Rise of Automation in Crane Systems
In recent decades, the crane industry has witnessed the rise of automation. Modern cranes are now equipped with advanced control systems that allow for remote operation, real-time monitoring, and even semi-autonomous functionalities. This shift has been driven by the need for increased precision, efficiency, and safety in industrial operations.
One of the key advancements in automated crane systems is the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology. IoT-enabled cranes are equipped with sensors that provide real-time data on load weight, machine health, and environmental conditions. This data is transmitted to central control systems, allowing operators to monitor crane performance and anticipate maintenance needs before a breakdown occurs.
In industries like warehousing and logistics, fully automated cranes are now commonplace. These cranes are capable of moving loads without human intervention, relying on pre-programmed instructions and real-time data from sensors. This reduces labor costs and improves operational efficiency, particularly in high-volume environments.
Benefits of Automated Crane Systems
The transition from manual to automated crane systems has brought about several key benefits for industries:
- Increased Precision: Automated cranes can lift and move loads with millimeter accuracy, reducing the risk of accidents and damage to goods.
- Enhanced Safety: By removing human operators from potentially dangerous situations, automated cranes minimize the risk of injuries.
- Higher Productivity: Automation allows faster and more consistent operations, reducing downtime and increasing output.
- Cost Savings: Although the initial investment in automated cranes may be higher, the long-term cost savings in labor, maintenance, and operational efficiency are substantial.
Challenges and Future Trends
While automated cranes offer numerous advantages, they also present challenges. The initial costs for implementing such systems can be prohibitive for smaller businesses, and there is a learning curve associated with adopting new technology. Additionally, the integration of IoT and other smart technologies requires robust cybersecurity measures to protect against data breaches and system disruptions.
Looking forward, the future of crane technology is likely to involve even greater levels of automation and connectivity. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are expected to play a larger role in optimizing crane operations, allowing machines to make real-time decisions based on data. Drones and other aerial technologies may also be used in conjunction with cranes to enhance monitoring and safety.
Conclusion
The evolution of crane technology from manual systems to automated powerhouses has transformed industries across the globe. As automation continues to advance, businesses that invest in modern crane systems will benefit from increased safety, precision, and efficiency. Understanding the history and potential of crane technology can help companies make informed decisions when choosing lifting solutions for their operations.
By embracing the future of crane automation, businesses can ensure they remain competitive in a fast-evolving industrial landscape.
By embracing the future of crane automation, businesses can ensure they remain competitive in a fast-evolving industrial landscape.
